Components
Concept of components
Each GIF instance manages different components. A component is a specific smart contract with a certain core functionality. The components can represent different core objects.
The core objects are:
-
Products
-
Oracles
-
Risk pools
All components and thus the objects they contain can assume identical states and have the same life cycle but can differ significantly in terms of lifespan.
Lifecycle
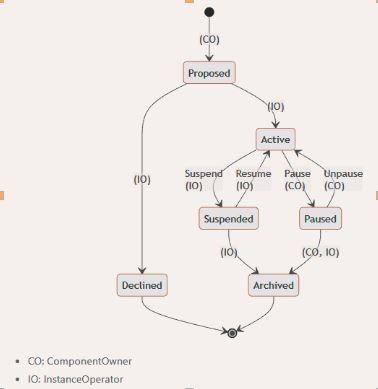
A component in the GIF is always in one of the following states:
-
Created
-
Proposed
-
Declined
-
Active
-
Paused
-
Suspended
-
Archived
The transition between these states and roles is described in the above diagram. The lifecycle of a component starts with its development and deployment on the blockchain.
The component owner can implement their requirements in the smart contract or use generic GIF components.
In the next step, the component is registered, approved, and activated by the instance operator in the GIF instance. The instance operator can also decline a component.
In the event of approval, the instance operator continues to check the technical and procedural details. The instance operator can also outsource the verification to an independent audit.
Another condition is that the component owner must contribute a certain amount of DIP token to be allowed to operate in the GIF instance. |
If the component is active, it can be used until it is set to either suspended or paused. The difference between suspended and paused is that only the instance operator can suspend a component or resume it from suspended to active. The component owner can set a component to paused, and the component owner and the instance operator can unpause the component.
If the component is inactivated (pause, suspended) and not reactivated (resume, unpause), it is not deleted but archived.
For each component type (products, oracles, risk pools), we provide sample implementations that you can use as a starting point for your implementation.
Products
A product is a specific smart contract that implements the functionality of this product. The product owner can implement its specific requirements, or he can use the generic functionality of the GIF.
After the product is technically developed and deployed to the blockchain, it must be registered in the GIF instance. This action is typically integrated with the deployment process.
The GIF instance offers the following functions to the product owner for this:
-
‘registerProduct’
After registering a product, it needs to be approved by the instance operator. The instance operator will check the details, such as that there is no malicious code in the product contract.
A possible and likely requirement is that the product owner stakes a certain amount of DIP token in a particular contract before actively selling products and earning money on the platform.
Approval is made by the instance operator using the function
-
‘approveProduct’
After approval of the product, the product is active and can start selling policies.
Should a change in terms imply a re-deployment of the product, the old product needs to be deactivated. For this, the GIF instance offers two functions:
-
‘pauseProduct’
-
‘unpauseProduct’
Oracles
Oracles are vital to the GIF, as they link the blockchain-based smart contracts and the index/parameter information necessary to operate real-world insurance products.
Products can utilize product-specific oracles, but they can also use generic oracles, which can, in turn, be implemented by many different parties.
An oracle owner can propose oracles he would like to offer (in the case of the oracle owner) or use (in the case of the product owner). The instance operator checks the suggested oracles and activates them after successfully checking. The instance operator can deactivate or remove the oracle if necessary.
The following functions are available for oracles:
-
proposeOracle (oracle owner)
-
activateOracle (instance operator)
-
deactivateOracle (instance operator)
-
removeOracle (instance operator)